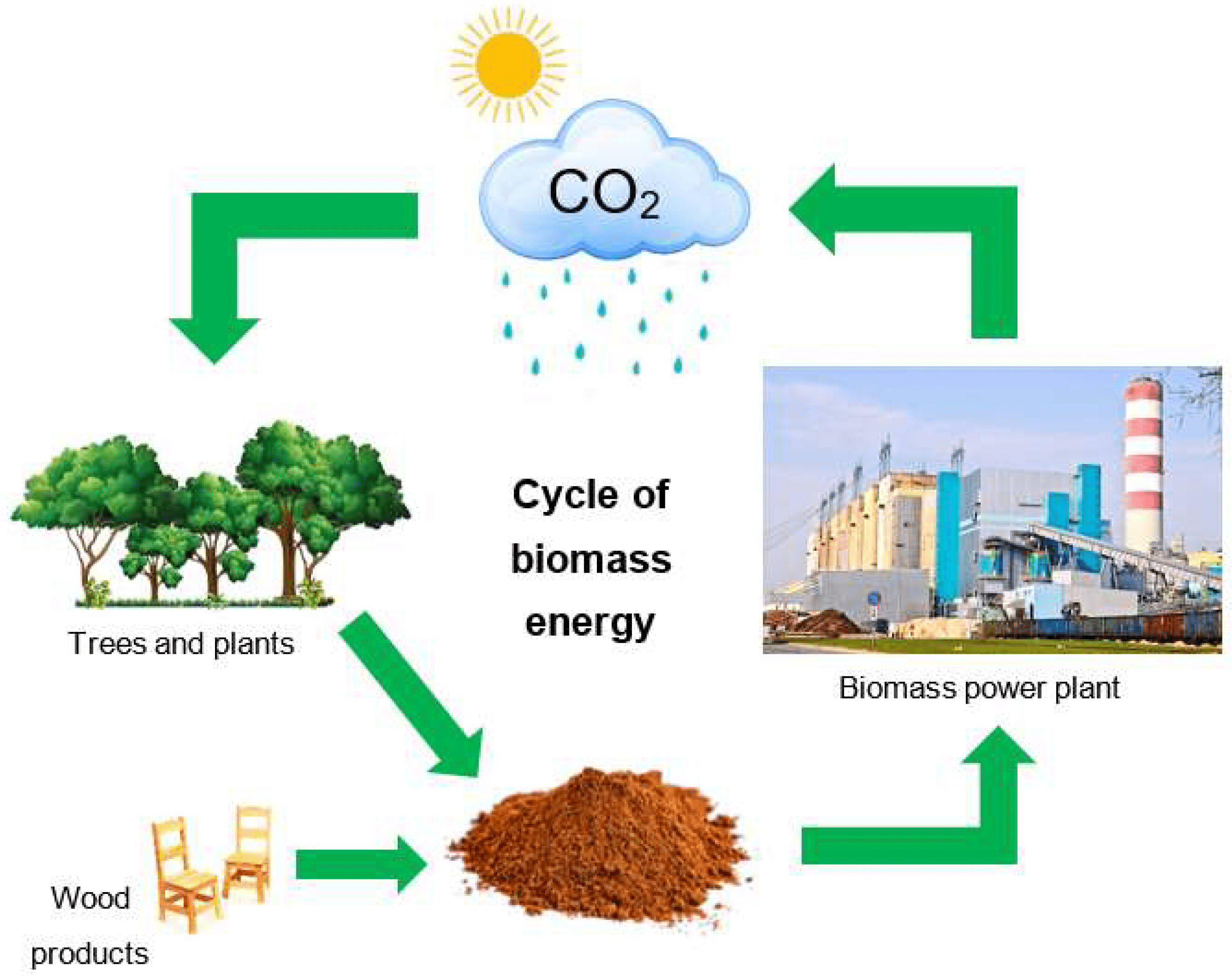
Harnessing Nature’s Power
Bioenergy, which draws from organic matter such as plants, crops, and waste, has emerged as a promising source of renewable energy. As global concerns about climate change and energy scarcity intensify, bioenergy offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. Unlike traditional energy sources that deplete finite resources and contribute to environmental degradation, bioenergy taps into natural processes, making it a vital component in the transition to a low-carbon future.
Addressing Energy Waste
One of the most compelling benefits of bioenergy is its ability to address energy waste. In many industrialized countries, a significant portion of energy is squandered due to inefficient practices, outdated technologies, and the failure to repurpose organic waste. Bioenergy can help reduce this waste by transforming organic materials that would otherwise end up in landfills or incinerators into valuable energy resources. This not only mitigates the environmental impact of waste but also contributes to a more efficient and circular economy.
Types of Bioenergy
Bioenergy is a versatile field, encompassing various technologies, each with distinct processes and applications. For instance, biomass energy is generated by burning organic materials such as wood, agricultural residues, or other plant matter to produce heat or electricity. This method, one of the oldest forms of energy production, has seen significant improvements in efficiency and cleanliness with modern advancements.
Another example is biofuels, which are liquid fuels made from plant-based materials. Biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, are primarily used in transportation and offer a renewable alternative to gasoline and diesel. They are produced from crops like corn, sugarcane, or algae.
Biogas, on the other hand, is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic matter, such as food waste, manure, or sewage. This process generates methane gas, which can be used for heating, electricity generation, or as vehicle fuel. Biogas systems are particularly valuable in waste management and rural energy supply, offering a sustainable way to handle organic waste while producing energy.
Finally, bioethanol, a type of biofuel, is made by fermenting sugars found in plants like corn or sugarcane. It is commonly blended with gasoline to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve fuel efficiency, representing a significant industry in countries with abundant agricultural resources.
Biomass, a Carbon-Neutral Fuel Source?
While biomass is often considered a carbon-neutral fuel source, its true environmental impact is more complex. While the burning of biomass releases carbon dioxide, it also sequesters carbon during the growth of the plants used to produce it. In theory, this creates a carbon-neutral cycle. However, the carbon neutrality of biomass depends on several factors, including the type of biomass used, its cultivation practices, and the efficiency of its conversion to energy. If the biomass is produced sustainably, with minimal deforestation and soil degradation, and if the energy conversion process is efficient, biomass can indeed be a carbon-neutral fuel source. However, if these conditions are not met, biomass can contribute to net greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the long-term sustainability of biomass production must be carefully considered to ensure that it does not deplete natural resources or harm ecosystems.
Environmental Benefits
Bioenergy offers a range of environmental benefits, making it a crucial component of sustainable energy strategies. When sourced and managed sustainably, bioenergy can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions by displacing fossil fuels. The carbon dioxide released during the combustion of biomass is roughly equivalent to the CO2 absorbed by the plants during their growth, resulting in a near-neutral carbon cycle.
Moreover, bioenergy contributes to cleaner air by reducing emissions of harmful pollutants such as sulfur dioxide and particulate matter, which are commonly associated with fossil fuel combustion. This improvement in air quality can have a positive impact on public health, particularly in urban areas where air pollution is a major concern.
Another significant advantage of bioenergy is its role in waste reduction. By utilizing organic waste for energy production, bioenergy helps divert waste from landfills and reduces the need for incineration. This not only lowers greenhouse gas emissions but also minimizes the environmental footprint of waste disposal.
Additionally, the bioenergy industry has the potential to create jobs, especially in rural areas where feedstock production and bioenergy facilities are often located. This can stimulate local economies and contribute to rural development, offering economic benefits alongside environmental ones.

Ecological and Climate Considerations
While bioenergy presents numerous benefits, it also poses challenges that require careful ecological and climate considerations. For instance, the production of biofuels, particularly those derived from crops, can compete with food production for land. This competition can lead to deforestation, habitat loss, and increased pressure on land resources. Sustainable land management practices are essential to avoid these negative impacts and ensure that bioenergy contributes to biodiversity conservation.
Furthermore, intensive bioenergy crop production can degrade soil health and increase water usage, particularly in regions already facing water scarcity. Implementing sustainable agricultural practices, such as crop rotation, reduced tillage, and water-efficient irrigation, is crucial to maintaining soil fertility and minimizing water use.
The large-scale production of bioenergy can also threaten biodiversity by replacing natural habitats with monoculture energy crops. Protecting natural ecosystems and promoting biodiversity-friendly bioenergy practices, such as using marginal lands and encouraging mixed cropping systems, are important for balancing energy production with ecological integrity.
In addition to these challenges, the impact of climate change on bioenergy production cannot be overlooked. Changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and the frequency of extreme weather events can affect crop yields and the availability of biomass feedstocks. Developing resilient bioenergy systems that can adapt to these changes is critical for ensuring the long-term sustainability of bioenergy.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many potential benefits, bioenergy is not without its challenges. Ensuring that bioenergy production is sustainable requires a careful balance of ecological, economic, and social factors. The sustainability of bioenergy hinges on responsible land use, soil health, water management, and the preservation of biodiversity. Certification schemes and government policies can help guide the responsible development of bioenergy, ensuring that it meets environmental standards and contributes to broader sustainability goals.
Economic viability is another consideration. The cost of bioenergy production can vary depending on factors such as feedstock availability, technology, and government policies. While bioenergy can be cost-competitive with fossil fuels in some regions, it may require subsidies or incentives to be economically viable in others.
Finally, advancing bioenergy technologies and expanding infrastructure are crucial for scaling up bioenergy production. This includes developing more efficient conversion processes, improving feedstock logistics, and integrating bioenergy into existing energy systems.
Related Content
- O-Wind Turbine: Revolutionizing Urban Wind Energy and Its Ecological Impact
- Motionless Wind Energy: A Quiet Revolution in Renewable Power
- A Balancing Act Between Renewables and Energy Security
- Nuclear Power: A Cornerstone of the Energy Transition?
- The Future of Renewable Energy: Innovations and Challenges
- The Rise of Renewables: Powering the Future with Clean Energy
- Bioenergy, a sustainable solution
- Waste to Energy: How Bioenergy is a Sustainable Solution
- Sustainability of bioenergy – Mapping the risks & benefits
- How bioenergy contributes to a sustainable future