The race to dominate space exploration is heating up. While NASA has long been the leader in advancing human capabilities in space, China has recently announced a groundbreaking technological leap that could potentially place it ahead of NASA and even Russia in the race to conquer the stars. According to reports from the South China Morning Post, Chinese researchers have unveiled a new plasma propulsion engine that outperforms conventional electric and hydrogen propulsion systems. This new engine, which promises to revolutionize space travel, could provide a faster, more efficient method for interplanetary missions, including the coveted goal of sending humans to Mars.
This development is not just a minor step forward; it’s a potential game-changer that may redefine how we think about space propulsion and exploration. As we delve into the specifics of this innovation, it’s important to understand how this new plasma engine works, how it compares to other propulsion technologies, and the wider implications this breakthrough could have on the future of space exploration.
The Plasma Engine: A New Era of Space Travel
For decades, the most efficient propulsion methods for space travel have relied on traditional rocket engines, which burn chemical fuel to propel spacecraft into orbit and beyond. While this technology has been effective for reaching the moon and sending unmanned probes to distant planets, it has its limitations, particularly when it comes to long-duration space missions. The need for more efficient propulsion methods became evident when space agencies like NASA began planning missions to Mars and other deep-space destinations.
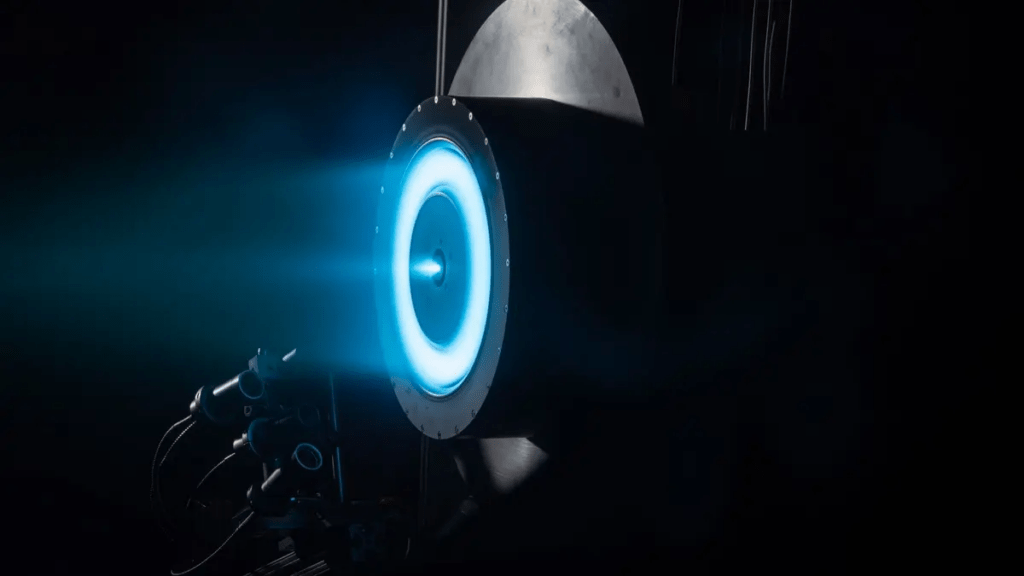
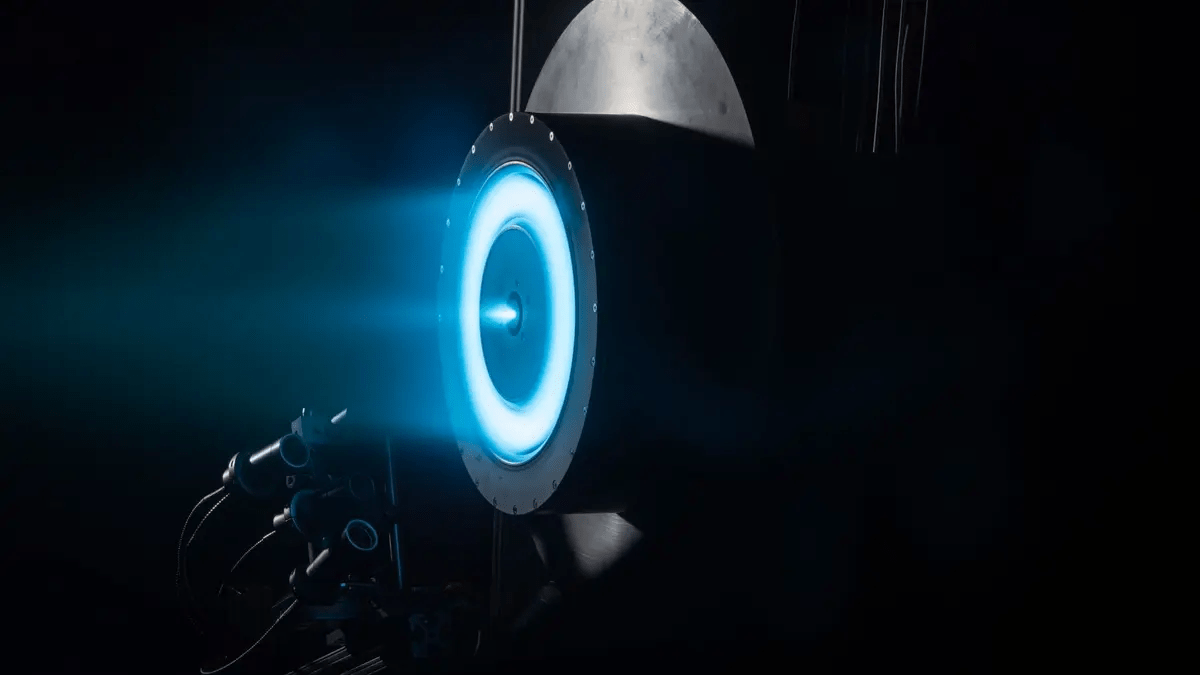
The newly unveiled Chinese plasma engine could be the answer to these challenges. Known as the “high-thrust magnetic plasma thruster,” this engine represents a significant leap in propulsion technology. Its key feature is the ability to operate stably at full power — 100 kilowatts — which is critical for deep-space missions that require consistent, long-duration thrust.
The Xi’an Aerospace Propulsion Institute, which developed the engine, described its successful ignition as a major breakthrough, positioning it at the forefront of global space propulsion research. The engine works by ionizing gases such as argon or xenon and releasing charged particles at extremely high speeds, creating a continuous thrust. This constant acceleration, combined with the engine’s efficiency, makes it far superior to traditional chemical rockets, which can only generate high thrust for short bursts.
How the Plasma Engine Works
Understanding how the plasma engine works requires a dive into the science of plasma physics. Plasma is often described as the “fourth state of matter” (after solid, liquid, and gas), and it is created when gases are heated to extremely high temperatures, causing atoms to ionize. This ionized gas, or plasma, is made up of positively charged ions and negatively charged electrons. The plasma engine utilizes this phenomenon to generate thrust.
The engine operates by using an electric field to accelerate the ionized gas particles, which are then expelled out of the engine at high velocity. Unlike traditional chemical rockets, which burn fuel to generate thrust, plasma engines rely on electricity to ionize the gas, which makes them far more energy-efficient. The constant acceleration of the plasma engine means that spacecraft powered by it could achieve much faster speeds over time, reducing the duration of long-distance space missions.
There are two key innovations that make China’s plasma engine particularly noteworthy: the use of 3D-printed parts and the integration of high-temperature superconducting magnets. The 3D-printed parts allow for more precise engineering, which improves both the durability and performance of the engine. Meanwhile, the superconducting magnets significantly enhance the efficiency of the engine by minimizing energy losses and boosting its overall power output. These innovations not only make the engine more effective but also pave the way for future advancements in space propulsion technologies.
Comparing China’s Engine to U.S. and Russian Technologies
The race for advanced space propulsion technologies is not limited to China. Russia, another major player in the field of space exploration, has also been working on its own plasma engine. In fact, Russia’s prototype plasma engine reportedly has the potential to reduce the travel time to Mars to just under two months, which is a drastic improvement compared to the current propulsion technologies that would require several years for the same journey.
While this is a significant achievement in its own right, it still doesn’t match the long-term efficiency that China’s engine offers. Currently, both the U.S. and Russia are focused on improving their electric propulsion systems, but these systems are still limited by the amount of power they can generate. The key challenge with these engines is their ability to produce a consistent thrust over extended periods, which is critical for missions that could last years, such as a manned mission to Mars.
The Chinese plasma engine, on the other hand, offers a new level of efficiency by continuously generating thrust without the need for fuel burning. Plasma propulsion engines also have the advantage of being much lighter and more compact than traditional chemical rockets, making them ideal for deep-space missions where payload weight is a crucial consideration. This new approach allows for a more reliable and sustainable method of propulsion, which could reduce the costs and risks associated with long-term space missions.
What makes China’s engine so promising is its ability to sustain high levels of thrust for longer periods, which significantly reduces mission times and increases fuel efficiency. In addition, the use of superconducting magnets allows the engine to generate a higher power output while using less energy, which could make it more suitable for long-duration missions to places like Mars, Jupiter, and even beyond. If the Chinese continue to refine this technology, they could soon surpass both the U.S. and Russia in the development of next-generation space propulsion systems.
Why This Matters for the Future of Space Exploration
The implications of China’s plasma engine extend far beyond just space propulsion. This development could have a transformative impact on the entire field of space exploration. With more efficient propulsion, spacecraft could travel to distant planets in a fraction of the time it would take using traditional rocket technology. This means that human missions to Mars, as well as other deep-space missions, could become a reality much sooner than previously anticipated.
The potential of the plasma engine is not just limited to manned missions to Mars. It could also be a game-changer for interplanetary cargo transport. Currently, sending materials to distant planets is a costly and time-consuming process. By using plasma propulsion, China could revolutionize how we transport goods and equipment to the outer reaches of the solar system, paving the way for more ambitious missions that would require substantial resources.
Furthermore, the technological advancements that come with developing plasma engines, such as the use of 3D printing and superconducting materials, could have applications in other areas of aerospace engineering. These innovations could lead to lighter, more durable spacecraft, as well as more efficient energy systems that could benefit a wide range of industries beyond space exploration.
The Global Implications of China’s Space Achievements
China’s growing capabilities in space exploration are rapidly catching the attention of the global community. As the country continues to invest in advanced space technologies, it is clear that it is positioning itself as a major player in the future of space exploration. This development in propulsion technology is a reflection of China’s larger ambitions to become a dominant force in space, rivaling, and perhaps even surpassing, the capabilities of established space agencies like NASA.
The Chinese government has made space exploration a key component of its long-term goals, and its ambitious space programs are a clear indicator of the country’s desire to lead the way in new frontiers. In recent years, China has achieved a series of significant milestones, including landing the Chang’e-4 spacecraft on the far side of the moon and launching the Tianwen-1 mission to Mars. Now, with the introduction of this revolutionary plasma engine, China is positioning itself at the forefront of the next phase of space exploration.
As competition in space heats up, NASA will be forced to step up its efforts to develop next-generation propulsion technologies. If China’s plasma engine proves successful, it could push NASA and other international space agencies to accelerate their own research into advanced propulsion systems. The result could be a new era of global collaboration or competition, where space agencies from around the world race to develop the most advanced technologies for exploring the cosmos.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the promising potential of the Chinese plasma engine, there are still several challenges that must be overcome before it can become a practical solution for space missions. The technology is still in its early stages, and further research and testing are required to ensure its reliability and performance under real-world conditions. Additionally, scaling the technology to power larger spacecraft for crewed missions will require overcoming significant engineering and material science challenges.
Another challenge that remains is the integration of this new propulsion system into existing space programs. Space agencies like NASA will need to develop new infrastructure and training programs to accommodate these advanced propulsion systems. As a result, it will take time before plasma propulsion engines become a regular part of space exploration missions.
Nevertheless, the progress made by China is undeniably significant. If the technology continues to develop at its current pace, it could soon become a vital tool for interplanetary travel, and China’s leadership in this field could reshape the future of space exploration. The race is on, and the world is watching closely as China takes bold steps forward into the final frontier.
Conclusion: A New Era of Space Exploration
The unveiling of China’s high-thrust magnetic plasma thruster marks a new chapter in the story of space exploration. By offering a more efficient, faster, and sustainable propulsion method, this breakthrough could pave the way for new space missions that were once thought impossible. Whether China will ultimately lead the charge in interplanetary travel or spark a new wave of innovation across the global space community remains to be seen. But one thing is clear: the future of space exploration is rapidly evolving, and China is firmly positioned at the cutting edge of this transformation.
Related Content
- France’s Massive Natural Hydrogen Reserve: A Game Changer for Clean Energy and the Planet
- Breakthrough in Energy: The First Production of “Pink Hydrogen”
- China Unveils Jupiter One: World’s Most Powerful Hydrogen Generator Achieves 443.45 Tons Per Hour Capacity
- AVL RACETECH’s Hydrogen Engine: A High-Performance Revolution
- Tesla’s Shift to Hydrogen Fuel Cells: A New Era of Innovation and Sustainability
- Kawasaki’s Hydrogen Motorcycle: A Step Toward Sustainable Motorcycling
- China’s Helium Breakthrough Could Boost Rocket Thrust by 300% – Inspired by a Boeing Failure – Orbital Today
- Yahoo is part of the Yahoo family of brands
- China’s progress on ‘game-changing’ space technology raises US concerns about closing gap | South China Morning Post
- Narrowing the gap between air and space travel
- Narrowing the gap between air and space travel – Opinion – Chinadaily.com.cn
- China’s Breakthrough in Reusable Launch Vehicle Engines!
- NASA cannot achieve it — China unveils “perfect fuel” to beat hydrogen and electrics