Introduction
Chronic inflammation is a persistent and prolonged immune response triggered by factors such as stress, poor diet, lack of exercise, environmental toxins, and underlying health conditions. Unlike short-term acute inflammation, chronic inflammation can lead to tissue damage and is associated with serious health issues. It is linked to conditions like cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune disorders, metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain cancers. Adopting natural strategies, including lifestyle changes and remedies, is crucial to counteract chronic inflammation and promote overall health.
Understanding Chronic Inflammation
Difference between Acute and Chronic Inflammation

Acute inflammation is the body’s immediate and beneficial response to injury or infection, characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain. It’s a short-lived process aimed at healing and protecting the body. Conversely, chronic inflammation is a prolonged, low-grade response that can persist for months or years. Unlike the noticeable symptoms of acute inflammation, chronic inflammation often occurs silently, quietly damaging tissues without obvious signs.
Causes and Contributors to Chronic Inflammation
Various factors contribute to the development of chronic inflammation. Unhealthy lifestyle choices such as a diet high in processed foods, excessive sugar intake, lack of physical activity, chronic stress, inadequate sleep, smoking, and exposure to environmental toxins can trigger and exacerbate chronic inflammation. Additionally, underlying health conditions like obesity, autoimmune disorders, and untreated infections can also fuel chronic inflammatory responses in the body.
Understanding the distinction between acute and chronic inflammation helps highlight the significance of addressing lifestyle factors and triggers that contribute to the prolonged inflammatory state.
Triggers of Chronic Inflammation
1. Unhealthy Diet:
- Highly Processed Foods: Processed foods high in refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives can promote inflammation.
- Excessive Sugar Intake: Consuming excessive amounts of sugar and high-fructose corn syrup can lead to increased inflammation levels.
- Unhealthy Fats: Trans fats and saturated fats found in fried foods and certain oils can contribute to inflammation.
2. Lack of Physical Activity:
- Sedentary lifestyles contribute to chronic inflammation. Regular exercise helps in controlling inflammation by producing anti-inflammatory cytokines.
3. Chronic Stress:
- Stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that, when chronically elevated, can promote inflammation in the body.
4. Inadequate Sleep:
- Not getting enough quality sleep can disrupt the body’s inflammatory processes, leading to increased inflammation.
5. Smoking and Environmental Toxins:
- Smoking and exposure to environmental pollutants and toxins can trigger an inflammatory response in the body.
6. Underlying Health Conditions:
- Certain health conditions like obesity, autoimmune disorders, untreated infections, and chronic diseases contribute to sustained inflammation.
Understanding these triggers empowers individuals to make informed lifestyle choices that mitigate chronic inflammation, emphasizing the importance of adopting anti-inflammatory habits and practices.
Natural Strategies to Reduce Chronic Inflammation
A. Healthy Diet
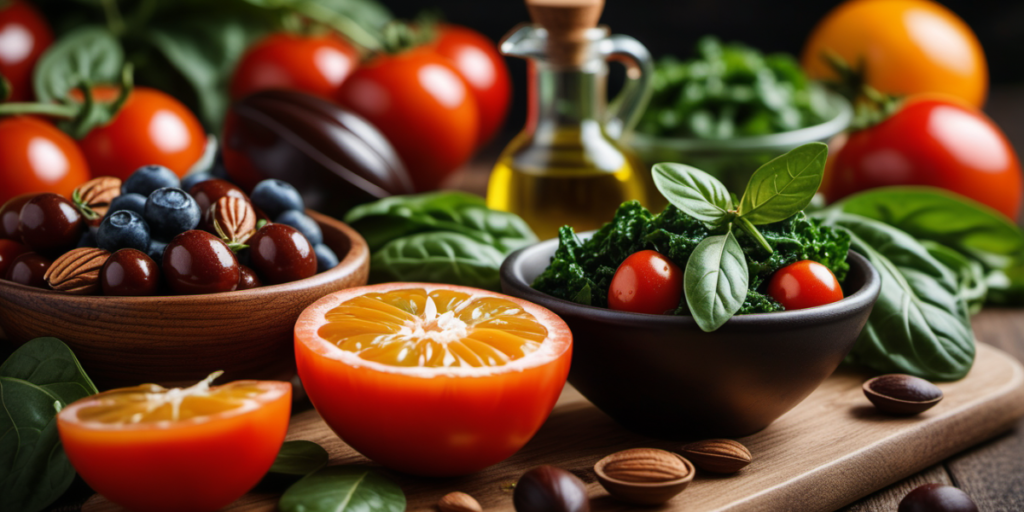
- Importance of an Anti-inflammatory Diet: An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on whole, nutrient-dense foods that possess anti-inflammatory properties, such as fruits, vegetables, fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and healthy fats like olive oil.
- Examples of Anti-inflammatory Foods: Berries, leafy greens, fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel), turmeric, ginger, garlic, and green tea are known for their anti-inflammatory effects.
- Foods to Avoid for Reducing Inflammation: Processed foods, refined sugars, excessive intake of red meat, and high-fat dairy products can exacerbate inflammation.
B. Regular Exercise
- Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits beyond just physical fitness. One significant advantage is its impact on managing inflammation within the body. Exercise triggers the release of anti-inflammatory substances, which can help mitigate chronic inflammation, a common precursor to various health issues. By engaging in regular physical activity, individuals can potentially lower their inflammation levels, thereby reducing the risk of developing inflammatory-related conditions.
- Moreover, exercise plays a pivotal role in enhancing overall immune function. It contributes to a more robust immune system, better equipped to fend off infections and illnesses. A well-functioning immune system is crucial for maintaining good health and resilience against diseases.
- When considering the types of exercises that prove beneficial in reducing inflammation, a diversified routine is key. Incorporating a combination of aerobic exercises, such as jogging, cycling, or swimming, aids in boosting cardiovascular health while also impacting inflammation positively. Additionally, strength training exercises, like weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, help build muscle mass and strength, which can further contribute to reducing inflammation markers.
- Furthermore, flexibility exercises, including yoga or stretching routines, play a crucial role in maintaining joint mobility and muscle flexibility. These exercises may indirectly assist in managing inflammation by improving overall bodily function and reducing stress, which can also impact inflammation levels.
- In essence, a well-rounded exercise regimen that includes aerobic, strength, and flexibility exercises is essential not only for physical fitness but also for managing inflammation and promoting a healthier immune system. Regular engagement in these various types of exercises can contribute significantly to one’s overall well-being and longevity.
C. Stress Management
- Connection Between Stress and Inflammation: Chronic stress can lead to elevated levels of cortisol, contributing to increased inflammation. Stress management techniques are vital in controlling this response.
- Techniques for Stress Reduction: Meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, mindfulness practices, and hobbies are effective in reducing stress and, subsequently, inflammation.
D. Sufficient Sleep
- Impact of Sleep on Inflammation: Quality sleep is crucial for regulating inflammatory responses in the body. Inadequate sleep can disrupt immune function and promote inflammation.
- Tips for Improving Sleep Quality: Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and maintaining a comfortable sleep environment are essential for better sleep quality.
E. Herbal Supplements and Spices
- Overview of Anti-inflammatory Herbs and Spices: Turmeric, ginger, garlic, green tea, cinnamon, and other herbs/spices possess potent anti-inflammatory properties.
- Incorporating Them into the Diet: Adding these herbs and spices to meals or consuming them as supplements can aid in managing chronic inflammation.
Anti-inflammatory Foods
Examples of Anti-inflammatory Foods:

- Foods to Avoid for Reducing Inflammation:
- Processed Foods: These often contain unhealthy fats, refined sugars, and additives that trigger inflammation.
- Refined Carbohydrates: White bread, pastries, and sugary cereals can contribute to inflammation.
- Excessive Alcohol: Heavy alcohol consumption can lead to increased inflammation in the body.
- Trans Fats: Found in fried foods, margarine, and many processed snacks, trans fats are notorious for promoting inflammation.
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet involves a shift towards whole, nutrient-dense foods while minimizing processed and inflammatory-inducing food choices.
Conclusion
Chronic inflammation poses health risks, emphasizing the need for natural strategies. Key approaches include a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, sufficient sleep, and herbal supplements. Consulting healthcare professionals is crucial, especially for those with existing health conditions. Embracing these strategies promotes overall health, offering a holistic approach to combat chronic inflammation and enhancing lifestyle balance.
Related Content
- Harvard Health Publishing
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH)
- HFU Health Liver Detox Tea Protect Liver & Lungs Improve Lung Function Suit For People Stay up and Alcohol Tea Polyphenols
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome’s Widespread Impact