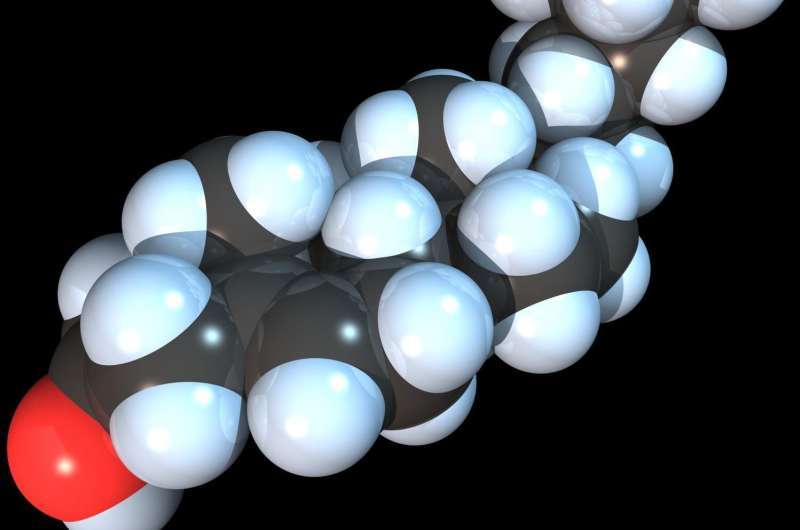
Precursor of Cholesterol Emerges as a Cell Protector: Unraveling the Antioxidant Role of 7-Dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC)
In a groundbreaking study led by Würzburg Professor José Pedro Friedmann Angeli, researchers have unveiled a surprising role for the cholesterol precursor, 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC), as a crucial antioxidant. The study demonstrates that 7-DHC integrates into cell membranes, shielding cells from a specific type of cell death known as ferroptosis.
“Until now, the accumulation of 7-DHC was only associated with neurodevelopmental defects. Now, we show that it increases cellular fitness and could potentially promote aggressive behavior in cancers like Burkitt’s lymphoma and neuroblastoma,” says Friedmann Angeli.
New Avenues for Cancer Treatment:
The discovery of 7-DHC’s protective function against ferroptosis presents exciting prospects for advancing cancer treatment and addressing diseases linked to this form of cell death. Friedmann Angeli notes, “It gives us new opportunities to test potential inhibitors targeting cholesterol biosynthesis that are already established in medical practice.”
The findings, published in the journal Nature, involved collaboration between the Würzburg team from the Rudolf Virchow Zentrum, scientists from Dresden University of Technology, Helmholtz Munich, University of Ottawa, and the German Cancer Research Center, DKFZ Heidelberg.
Cholesterol Levels and Cellular Fitness:
In a paradigm-shifting revelation, the traditional association between high cholesterol levels and health issues like heart disease and diabetes is given a fresh perspective. While most studies have concentrated on the direct contributions of cholesterol to these diseases, the discovery of 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC) as an antioxidant introduces an innovative dimension. This groundbreaking finding not only expands our understanding of cholesterol’s role but also opens up avenues for exploring changes in 7-DHC levels, offering a unique vantage point to gain crucial insights into various diseases beyond the cardiovascular spectrum.
Furthermore, the implications of 7-DHC’s newfound role extend to potential advancements in medical treatment. Researchers propose that drugs specifically designed to inhibit 7-DHC production should be investigated in tandem with other medications. This synergistic approach holds promise for yielding substantial benefits in the treatment of certain cancers. By targeting the inhibition of 7-DHC production, researchers aim to harness its potential in conjunction with established medications, introducing a novel therapeutic strategy that may prove effective in enhancing treatment outcomes for specific types of cancer. The intersection of cholesterol metabolism and cancer treatment opens up a new frontier in medical research, inviting exploration into the intricacies of cellular processes and signaling pathways that could pave the way for more targeted and effective therapeutic interventions.
Unraveling Tumor Development Effects:
The research journey led by Professor José Pedro Friedmann Angeli and his team takes an intriguing turn as they set their sights on investigating the impact of 7-DHC accumulation during tumor development. This ambitious research goal aims to delve into the nuanced role that 7-DHC might play in shaping the trajectory of tumor growth. Understanding how 7-DHC levels influence the intricate processes associated with tumor development holds promise for unraveling new dimensions in cancer biology and potentially identifying novel targets for therapeutic intervention. This phase of the study marks a crucial step toward bridging the existing knowledge gaps and advancing our understanding of the dynamic interplay between cholesterol precursors and tumorigenesis.
Simultaneously, the team advocates for additional epidemiological studies to shed light on the potential effects of drugs modulating ferroptosis, with a specific focus on widely prescribed medications like trazodone. The extensive usage of trazodone in the USA, often prescribed for insomnia, raises questions about its impact on plasma levels of 7-DHC and, consequently, its potential influence on ferroptosis-related processes. By calling for further epidemiological investigations, Friedmann Angeli and his team seek to unravel the intricate connections between these medications and critical aspects of public health, including cancer incidence, the occurrence of metastases, and other consequential health outcomes. This dual approach, combining in-depth tumor development studies and comprehensive epidemiological analyses, underscores the comprehensive and multi-faceted nature of the research endeavor, pointing towards a more profound understanding of the implications of 7-DHC and ferroptosis-modulating drugs in the realm of cancer research and public health.
FDA-Authorized Drugs and Potential Connections:
In a groundbreaking study led by Professor José Pedro Friedmann Angeli, researchers have unveiled a surprising role for the cholesterol precursor, 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC), as a crucial antioxidant. The study demonstrates that 7-DHC integrates into cell membranes, shielding cells from a specific type of cell death known as ferroptosis.
“Until now, the accumulation of 7-DHC was only associated with neurodevelopmental defects. Now, we show that it increases cellular fitness and could potentially promote aggressive behavior in cancers like Burkitt’s lymphoma and neuroblastoma,” says Friedmann Angeli.
While high cholesterol levels are traditionally linked to health issues like heart disease and diabetes, the focus of most studies has been on the direct contributions of cholesterol to these diseases. The discovery of 7-DHC as an antioxidant introduces a new dimension, opening up possibilities for studying changes in 7-DHC levels to gain crucial insights into various diseases. Moreover, researchers suggest that drugs targeting the inhibition of 7-DHC production should be explored in combination with other medications, offering potential benefits in the treatment of certain cancers.
Highlighting the link between the DHCR7 enzyme and 7-DHC production, Friedmann Angeli notes that drugs like trazodone, widely prescribed to combat insomnia and authorized by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have exhibited an intriguing impact on plasma levels of 7-DHC. The implications of this finding prompt further investigation into the potential links between ferroptosis-modulating drugs and critical aspects of public health, including cancer incidence and the occurrence of metastases.
Friedmann Angeli emphasizes the imperative need for epidemiological studies to discern the broader impact of ferroptosis-modulating drugs. Specifically, he underscores the importance of understanding whether patient groups regularly consuming such drugs, like trazodone, exhibit correlations with cancer incidence, metastases occurrence, or other vital elements of public health. This call for comprehensive epidemiological research hints at the potential far-reaching consequences of medications that influence ferroptosis, sparking interest in unraveling intricate connections between drug regimens and broader health outcomes.
As the scientific community embarks on an exploration of the multifaceted role of 7-DHC, this groundbreaking study opens unprecedented avenues for understanding cellular function and devising novel cancer treatments. The revelation that 7-DHC serves as a key antioxidant, preventing ferroptosis, not only expands our knowledge of cellular resilience but also offers tangible prospects for refining cancer therapies. The intricate interplay of cholesterol precursors in maintaining cellular health emerges as a captivating area of study, promising transformative insights into the delicate balance that governs cell survival and death. This pioneering research serves as a beacon guiding future investigations into the potential therapeutic applications and broader implications of manipulating cholesterol pathways in the pursuit of improved public health
Related Topics:
- The Malaria Vaccine Unveiling Surprising Health Benefits for Children – Micro2media
- Breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s Research: A Comprehensive Overview – Micro2media
- A cholesterol precursor mediates sensitivity to cell death by ferroptosis
- A cholesterol precursor mediates sensitivity to cell death by ferroptosis | About us