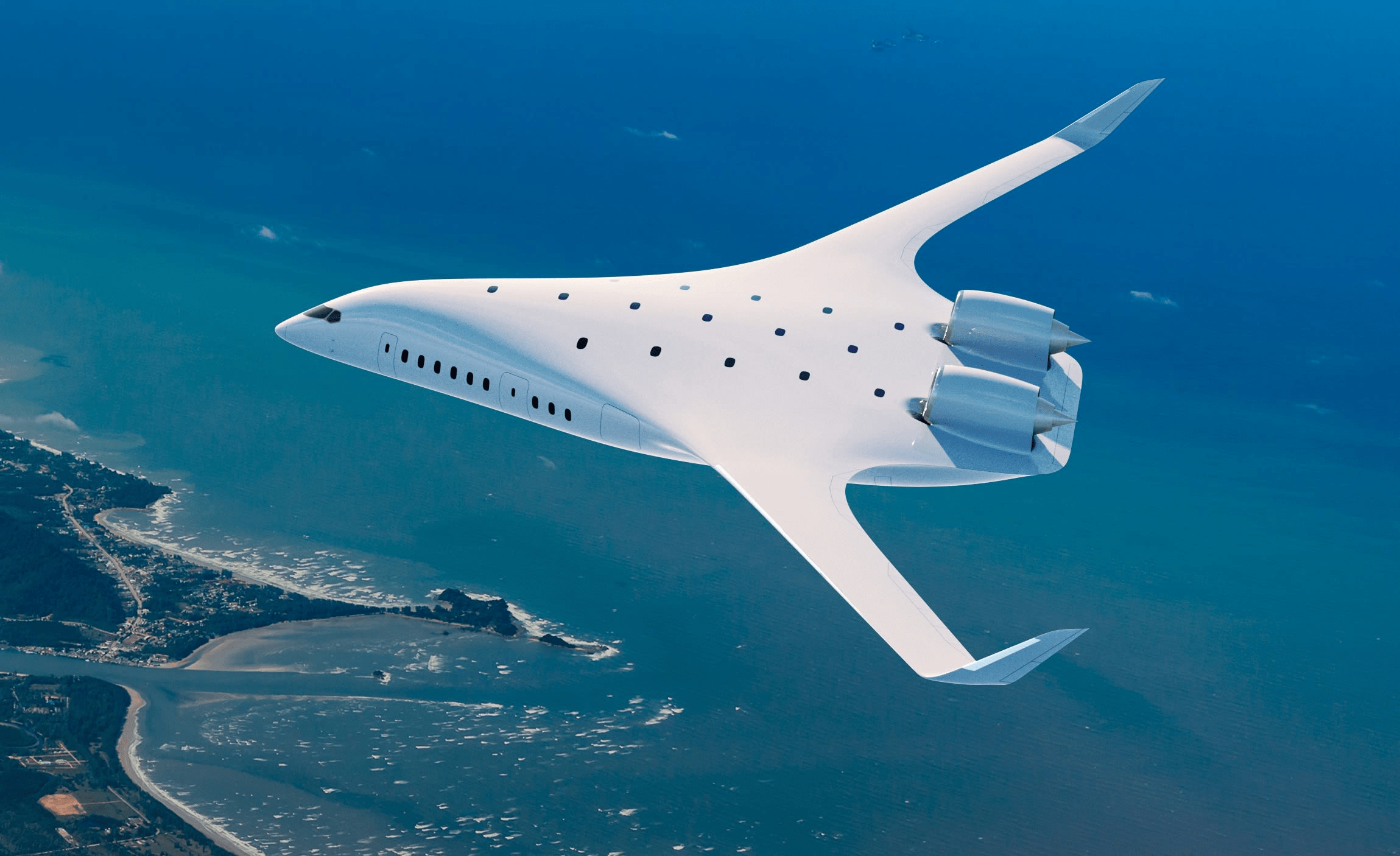
The aviation industry is on the brink of a transformative leap with the development of a new passenger plane featuring a “blended wing” design. This innovative aircraft, set to take to the skies by 2030, promises to cut fuel consumption by 50% and significantly reduce noise pollution. As the world grapples with the urgent need to address climate change and reduce carbon emissions, this breakthrough highlights the potential for sustainable innovation in aviation. Beyond its immediate benefits, the blended-wing design also underscores the importance of rethinking traditional systems to align with ecological goals.