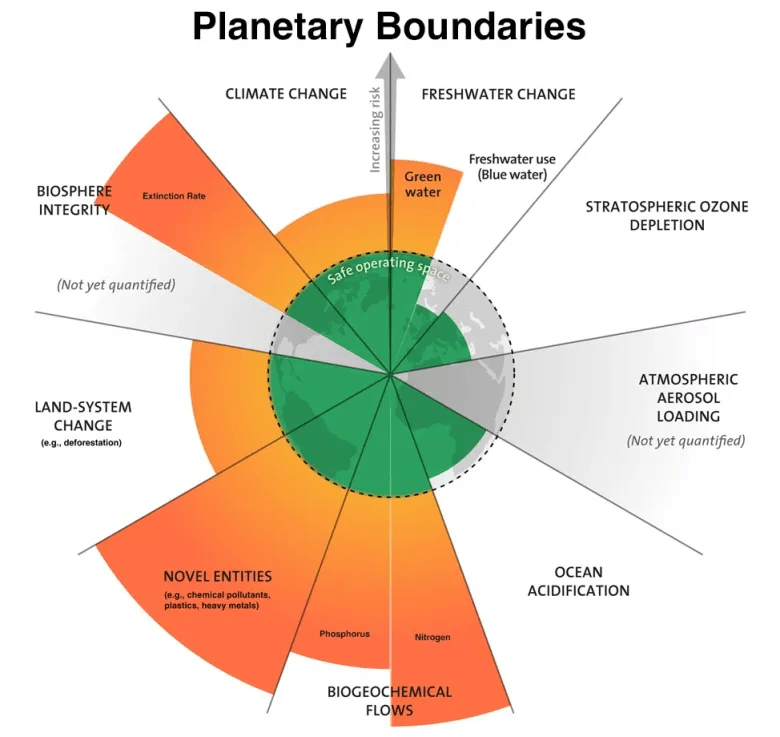
Ocean acidification, driven by the absorption of excess carbon dioxide by the oceans, threatens to become the seventh planetary boundary that humanity crosses. This phenomenon is already destabilizing marine ecosystems, impacting biodiversity, and endangering food security for millions. While six boundaries, including climate change and biodiversity loss, have already been breached, ocean acidification could compound these issues with far-reaching consequences. To avoid this outcome, immediate and coordinated global efforts are required to reduce carbon emissions, transition to renewable energy, restore ecosystems, and develop sustainable solutions for both marine life and human communities. The urgency of addressing ocean acidification highlights the interconnectedness of environmental issues and the critical need for international cooperation.