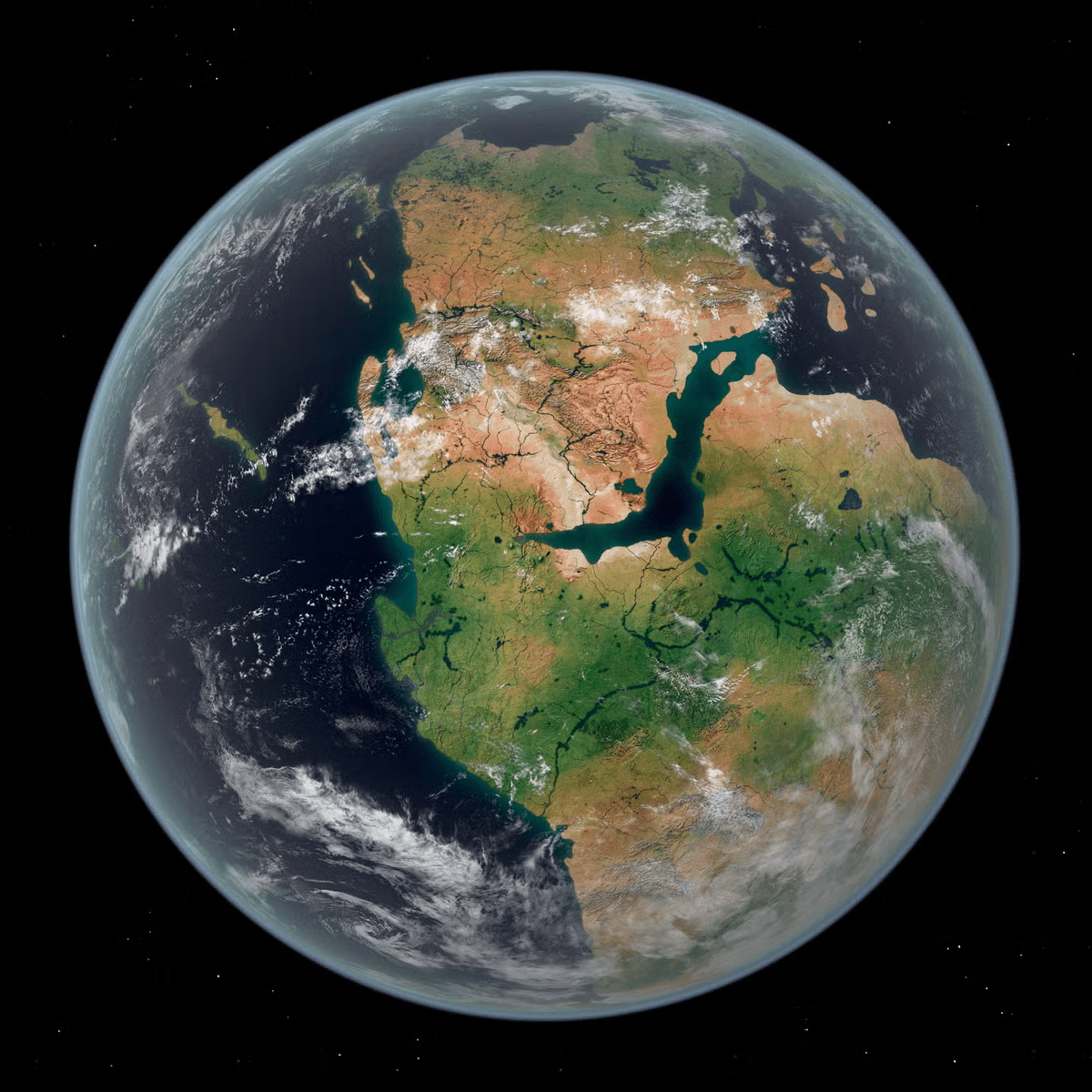
Earth’s tectonic plates are perpetually in motion, reshaping the surface of the planet over millions of years. This relentless process is predicted to culminate in the formation of a new supercontinent, named Pangea Ultima, approximately 250 million years from now. While this may seem like an event far removed from today, the implications of such a phenomenon provide a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of geological and climatic systems and their potential threats to life on Earth.
This article explores the key findings of recent scientific studies on the future formation of a supercontinent, its environmental impacts, and the lessons humanity can learn to address present-day climate challenges.
Understanding the Formation of Pangea Ultima
Pangea Ultima will be the result of the continuous movement of tectonic plates. Over hundreds of millions of years, the Earth has undergone cycles of supercontinent formation and breakup. Pangea Ultima represents the next phase in this cycle, where continents merge into a singular massive landmass.
The reshaping of the Earth’s continents, as exemplified by the predicted formation of Pangea Ultima, is a process fundamentally driven by several powerful geological forces. Plate tectonics, the primary engine of continental drift, involves the gradual movement of Earth’s lithospheric plates across the semi-fluid asthenosphere, causing continents to shift their positions over vast stretches of time. Subduction zones play a crucial role in this process; these are areas where one tectonic plate is forced beneath another, a phenomenon that can draw continents closer together as the Earth’s crust is recycled into the mantle. Furthermore, the reconfiguration of ocean basins significantly influences the distribution of landmasses, as changes in sea level and the shape of ocean floors can create or eliminate land bridges and alter coastlines. While the assembly of Pangea Ultima is projected to occur over an immense geological timescale, the eventual environmental consequences of such a continental amalgamation are expected to be profound, potentially triggering significant shifts in global climate patterns and impacting ecosystems across the planet.
Key Findings: Environmental and Biological Impacts
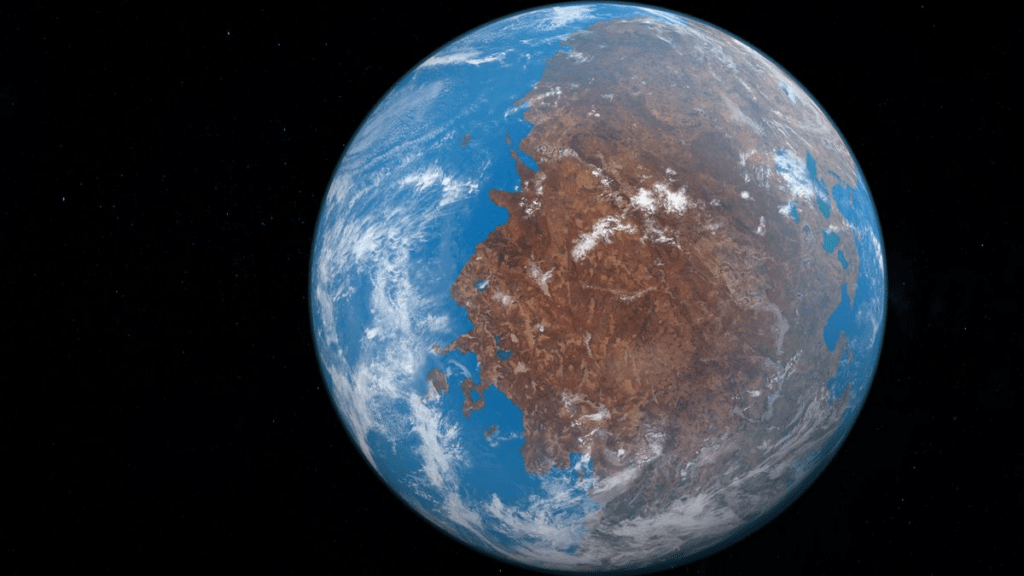
The formation of the supercontinent Pangea Ultima is projected to have profound environmental and biological impacts, with several key findings highlighting the severity of these changes. One of the most significant consequences is the likelihood of extreme global heat. The merging of continents into a supercontinent is expected to exacerbate global temperatures due to a combination of factors. Over the vast timescales involved, solar radiation reaching Earth will intensify as the sun grows hotter. Furthermore, the altered continental configuration will disrupt atmospheric circulation patterns, leading to a runaway greenhouse effect where heat is trapped more efficiently. This warming will be compounded by increased volcanic activity during the tectonic rearrangements, which will release substantial amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, further intensifying the greenhouse effect. These extreme heat conditions would render the majority of the supercontinent uninhabitable; current models estimate that only a small fraction, perhaps 8% to 16% of the landmass, might remain suitable for mammalian life.
Another critical impact involves volcanic activity and atmospheric changes. As tectonic plates collide and subduct during the formation of Pangea Ultima, a surge in volcanic activity is anticipated. This increased volcanism will emit massive quantities of greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide and methane, into the atmosphere. These emissions will drastically alter the atmospheric composition, contributing to further global warming and potentially reducing oxygen levels in certain regions.
The combination of extreme heat and other environmental stressors will lead to a significant loss of habitable land. With most of the supercontinent experiencing intolerably high temperatures, viable ecosystems for humans and other mammals will shrink dramatically. The prevalence of deserts and arid regions will expand, while coastal zones, which typically support rich biodiversity, will diminish due to the consolidation of landmasses.
The extreme environmental changes accompanying Pangea Ultima’s formation raise the potential for a mass extinction event. The projected severity of these conditions suggests that many mammals, including humans, may face an inability to adapt quickly enough to survive the extreme heat and limited resources.
Lessons for Today: The Parallels with Human-Induced Climate Change
The predicted consequences of Pangea Ultima’s formation mirror many effects currently attributed to anthropogenic climate change:
- Rising Temperatures: Human activities have already triggered global warming, with temperatures rising at unprecedented rates.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The release of carbon dioxide from fossil fuels parallels the volcanic emissions expected during supercontinent formation.
- Habitat Loss: Climate change is shrinking habitable zones, particularly in vulnerable regions such as coastal areas and arid zones.
These parallels underscore the urgency of addressing climate change to mitigate its effects and ensure a livable planet for future generations.
Mitigation Strategies: Learning from Future Predictions
While the formation of Pangea Ultima remains a distant event on a geological timescale, its study offers valuable insights into the intricate workings of Earth’s climatic and geological systems. These insights derived from modeling and predicting such a future supercontinent can significantly inform and guide current strategies aimed at combating climate change. A paramount strategy is the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Concerted global efforts to curb the release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere are critical. This necessitates a large-scale transition away from fossil fuels and towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal power. Furthermore, improving energy efficiency across all sectors, including transportation, industry, and buildings, is essential to minimize energy demand. The protection and expansion of carbon sinks, such as forests and oceans, which naturally absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, also play a vital role in mitigating climate change.
In addition to mitigating the causes of climate change, enhancing climate resilience is crucial to adapt to the inevitable changes already underway and those projected to worsen. Preparing for a hotter future involves strategic investments in resilient infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, droughts, and floods. The development of heat-resistant crops through advanced agricultural techniques is necessary to ensure food security in a changing climate. Similarly, safeguarding water resources through efficient management and conservation strategies is essential to address potential water scarcity.
Finally, promoting robust international cooperation is of utmost importance. The global nature of climate change demands collective solutions and coordinated action. Strengthening and upholding international agreements, such as the Paris Accord, is crucial to establish frameworks for countries to work together effectively in reducing emissions, sharing technologies, and providing support to vulnerable nations.

Ethical and Philosophical Reflections
The study of Pangea Ultima invites deeper reflection on humanity’s place within Earth’s long history. Geological events like supercontinent formation highlight the transience of human existence and the enduring power of natural systems. It is a humbling reminder that:
- Adaptation and Cooperation: Humanity’s survival hinges on its ability to adapt to environmental challenges and cooperate on a global scale.
- Stewardship of the Planet: As stewards of Earth, we have a moral obligation to preserve its habitability for future generations.
Conclusion
The formation of Pangea Ultima, though a distant event, serves as a powerful metaphor for the challenges posed by climate change today. The extreme heat, environmental disruptions, and potential mass extinction predicted for the supercontinent highlight the stakes of inaction. While humanity cannot alter tectonic processes, it can address the human-induced factors accelerating global warming and habitat loss.
By taking bold and immediate action, we can chart a course toward a sustainable future, ensuring that Earth remains a thriving home for all its inhabitants. The lessons from Pangea Ultima are clear: the choices we make today will shape the world of tomorrow.
Related Content
- ‘Supercontinent’ could make Earth uninhabitable in 250m years, study predicts | The Guardian
- Supercontinent tectonics and biogeochemical cycle: A matter of ‘life and death’ – ScienceDirect
- New ‘supercontinent’ could wipe out humans and make Earth uninhabitable, study suggests | CNN
- How did Pangea’s formation affect life on Earth? | Britannica
- Earth Ends 13-Month Streak of Record Heat: What Comes Next?
- The Unexpected Greening of Earth’s Drylands: A Double-Edged Sword for the Environment
- Earth Has Six Continents, Not Seven: Radical New Study with Ecological and Sustainability Solutions
- Forests: Earth’s Methane Guardians
- Protecting the Earth: The Critical Role of Ozone Gases
- 15 Earth-Friendly, Plastic-Free Products for a Sustainable Home